In a time when our everyday life is often characterized by fast food and processed foods, superfoods are coming into focus as true nutrient bombs. These special foods are distinguished by an exceptionally high concentration of vitamins, minerals, antioxidants and other bioactive substances. But what makes a food a superfood and how can you optimally integrate these powerful nutrient suppliers into your everyday life?
What are superfoods?
The term "superfood" is not scientifically defined, but it describes foods with an exceptionally high nutrient density. These natural powerhouses contain above-average amounts of health-promoting substances per calorie and can make a valuable contribution to a balanced diet contribute.
It is important to understand that superfoods are not miracle cures. They unfold their positive effects best as part of a varied and balanced diet. The combination of different nutrient-rich foods often enhances their health effects through synergistic actions.
The 15 Most Important Superfoods and Their Health Benefits
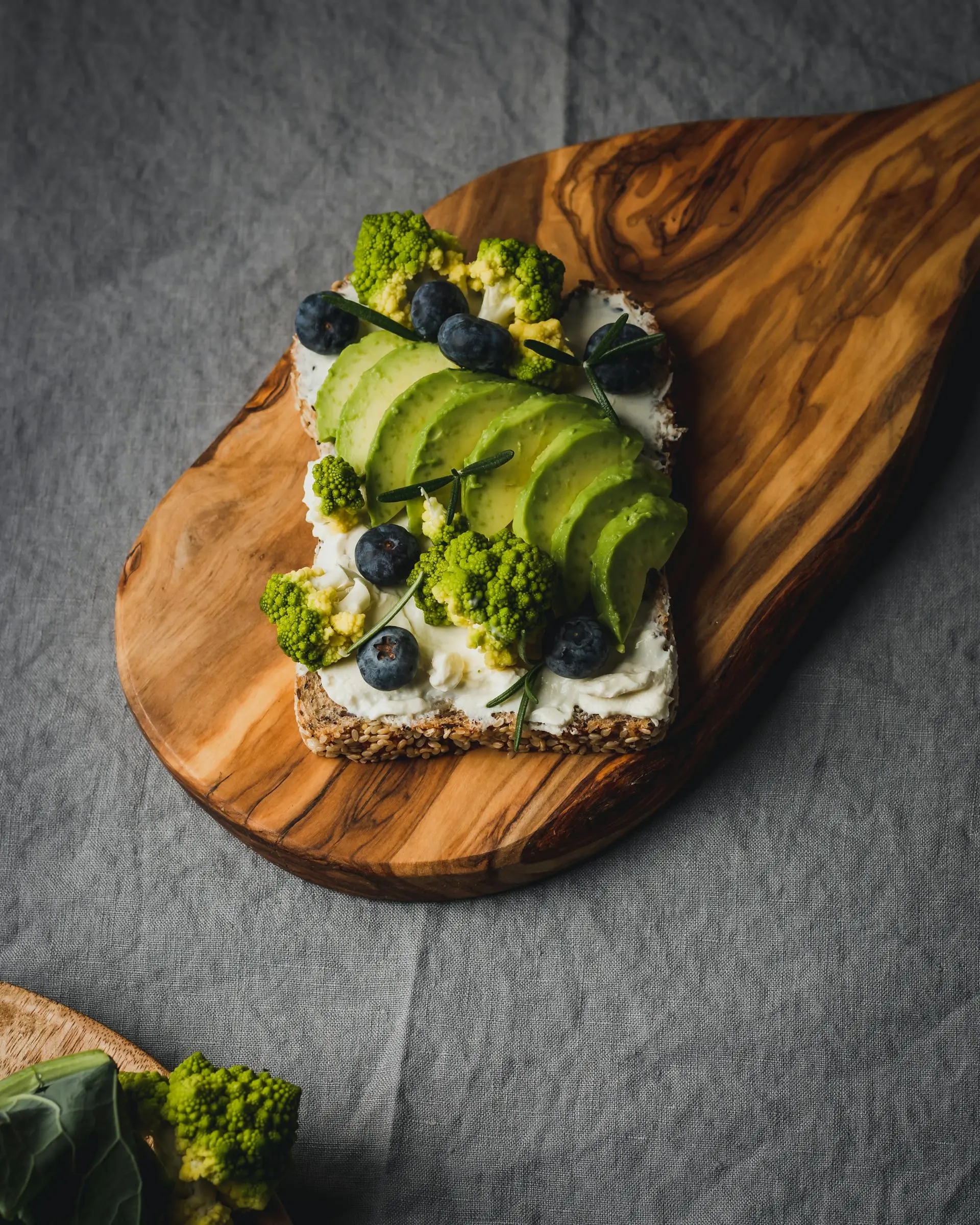
1. Blueberries
Blueberries are considered true antioxidant bombs. The anthocyanins they contain protect cells from oxidative stress and can improve memory performance. Studies show that regular blueberry consumption promotes heart health and has anti-inflammatory effects.
2. Spinach
Green leafy vegetables are rich in iron, folic acid, vitamin K, and lutein. Spinach supports blood formation, strengthens bones, and can improve athletic performance thanks to its high nitrate content.
3. Avocados
The creamy fruit provides healthy unsaturated fats, potassium, and vitamin E. Avocados can positively influence cholesterol levels and improve the absorption of fat-soluble vitamins from other foods.
4. Quinoa
The gluten-free pseudocereal contains all essential amino acids and is rich in fiber, magnesium, and iron. Quinoa is particularly suitable for vegetarian and vegan diets as a high-quality protein source.
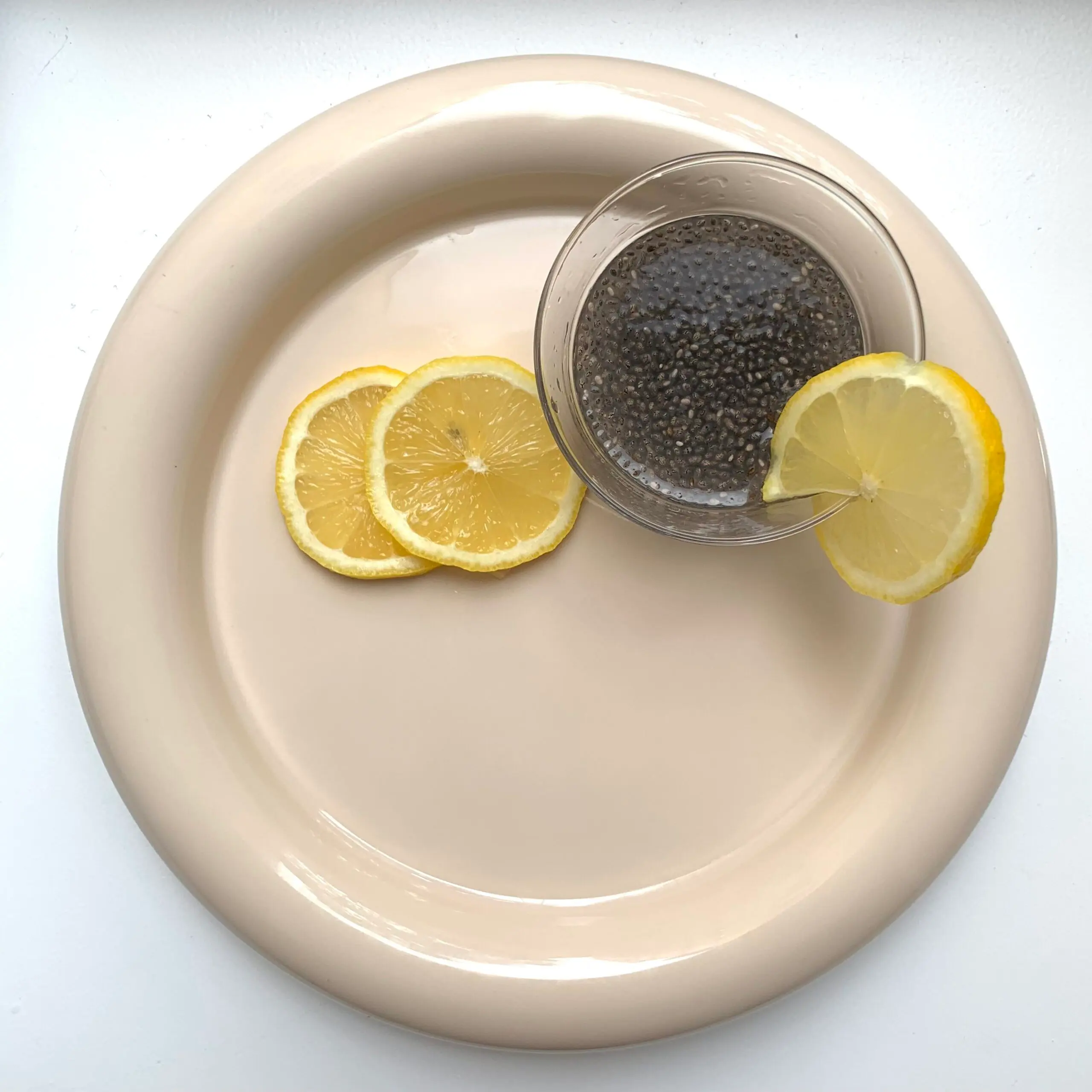
5. Chia seeds
The small seeds are true omega-3 powerhouses and also contain a lot of calcium, phosphorus, and fiber. They can help with weight loss as they swell significantly and keep you full longer.