Other Treatment Methods
.webp)
Farsightedness (hyperopia, hypermetropia)
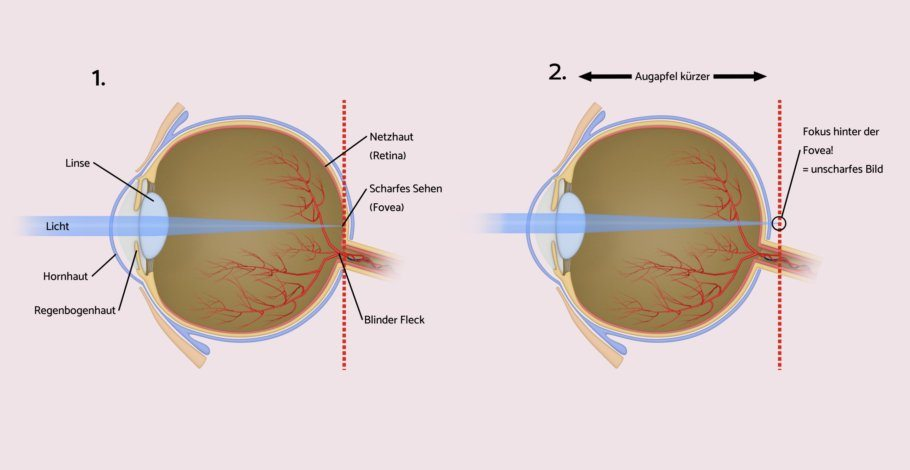
Whoever can only decipher the text in the newspaper or the message on the phone when they hold it further from the eye is suffering from farsightedness. Affected individuals either have an eyeball that is too short (axial hyperopia) or, as occurs more rarely, have to live with refractive hyperopia, a lack of refractive power in the interaction of phone the cornea, vitreous body and lens of the eye. Nature has arranged it so that a mild farsightedness in younger people can be more or less compensated for by so-called accommodation, namely by the tension of the ciliary muscle. However, with increasing age or severity of farsightedness, this ability diminishes. In addition, people with an eyeball that is too short develop an increased risk of contracting corneaglaucoma (Green Star).
L improvement in vision for farsightedness
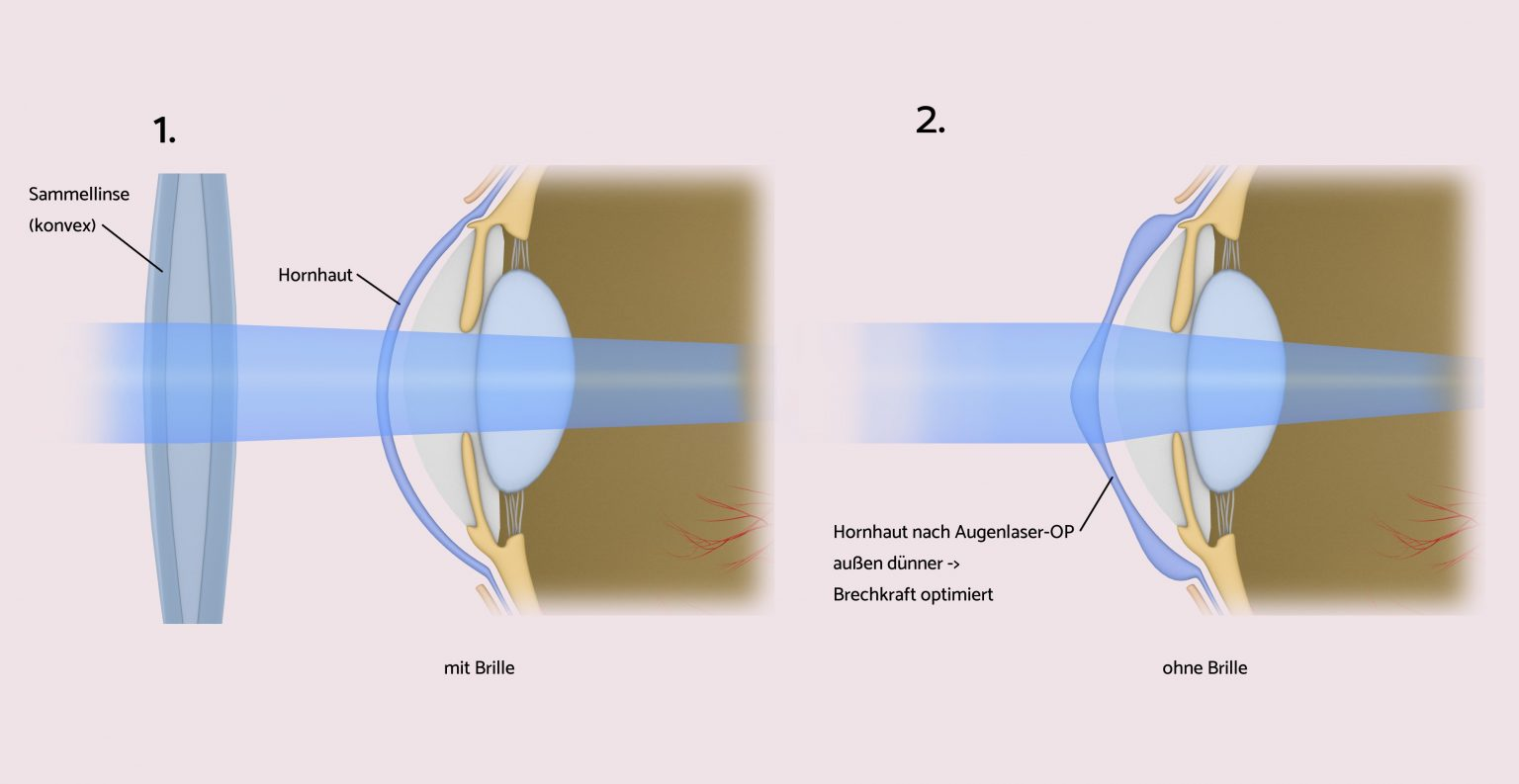
Usually, the ophthalmologist prescribes glasses or contact lenses. However, excellent results and, above all, a life without glasses are achieved by treatment with the eye laser. The LASIK method is generally suitable if the cornea is not too thin and the diopter values have not changed over a longer period of time. The high-tech variant of the LASIK procedure is the use of the Femtosecond lasers, die mit Abstand präziseste Vorgehensweise. Ist die Weitsichtigkeit besonders stark ausgeprägt, kommt auch der Einsatz einer künstlichen Linse in Frage, die die Brechkraft der eigenen natürlichen Linse unterstützt.
Procedure of the operation
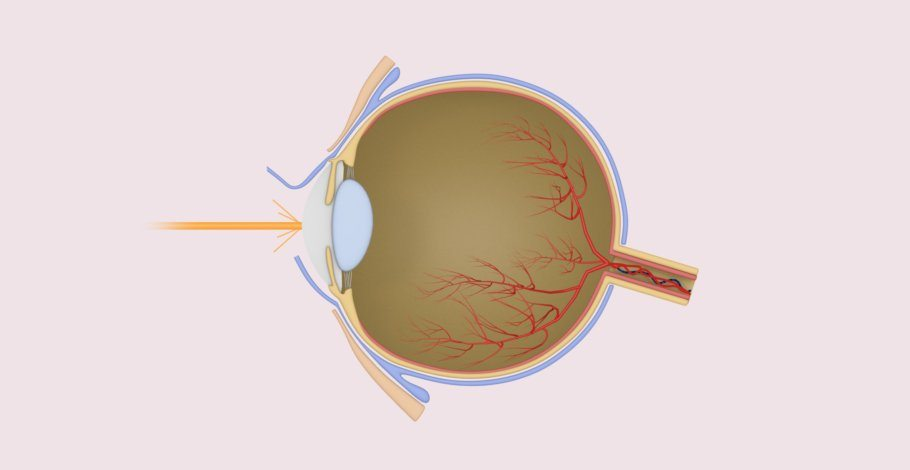
The surgical correction of farsightedness is often done through the use of modern laser technologies or the use of artificial lenses. One of the most common methods is the LASIK treatment (Laser-in-situ-Keratomileusis). This involves first making a thin incision in the top corneal layer (flap) with a special device. This is carefully folded to the side to work on the area underneath. An excimer laser is then used to precisely shape the cornea and improve its refractive power. The flap is then placed back where it naturally heals back into place.
A more advanced variant is the use of the Femtosecond lasers, which work particularly precisely and increase the accuracy of the LASIK method. This high-tech technology minimizes risks and ensures precise results.
In cases of more pronounced farsightedness, or if laser treatment is not suitable, an intraocular lens (IOL) to be implanted. In this case, either the natural lens is removed and replaced by an artificial lens, or an additional lens is used to support the natural lens. This procedure is usually performed under local anesthesia and enables a long-term improvement in visual acuity.
After the operation
After eye surgery, such as LASIK treatment or the implantation of an artificial lens, it is important to take certain precautions to ensure optimal healing and avoid complications. Immediately after the procedure, mild discomfort such as a foreign body sensation, light sensitivity, or watery eyes may occur. These symptoms usually subside within a few days.
Experts for this Treatment Method

- Modern Ophthalmology
Dr. Mirka R. Höltzermann
Augenpraxis Dr. Höltzermann, Dr. von Schnakenburg, Augenpraxis Dres. Höltzermann & von Schnakenburg
- Modern Ophthalmology
Dr. med. Ilya Kotomin
Smile Eyes Leipzig
- Modern Ophthalmology
Raphael Neuhann (FEBO)
Opthalmologikum Dr. Neuhann / Augentagesklinik am Marienplatz
- Modern Ophthalmology
Dr. med. Tabitha Neuhann
Opthalmologikum Dr. Neuhann / Augentagesklinik am Marienplatz
- Modern Ophthalmology
Prof. Dr. med. Tanja M. Radsilber
Augenzentrum Prof. Dr. med. Holzer & Prof. Dr. med. Rabsilber
- Modern Ophthalmology
Dr. med. Karsten Klabe
Breyer, Kaymak & Klabe AugenchirurgieAll Experts in this Department
Show All
- Modern Ophthalmology
Dr. Mirka R. Höltzermann
Augenpraxis Dr. Höltzermann, Dr. von Schnakenburg, Augenpraxis Dres. Höltzermann & von Schnakenburg
- Modern Ophthalmology
Dr. med. Ilya Kotomin
Smile Eyes Leipzig
- Modern Ophthalmology
Priv.-Doz. Dr. med. Daniel Pilger
Smile Eyes Berlin
- Modern Ophthalmology
Raphael Neuhann (FEBO)
Opthalmologikum Dr. Neuhann / Augentagesklinik am Marienplatz
- Modern Ophthalmology
Dr. med. Tabitha Neuhann
Opthalmologikum Dr. Neuhann / Augentagesklinik am Marienplatz
- Modern Ophthalmology