Stress has become omnipresent in our modern society. Occupational pressure, family obligations, and constant availability cause our stress hormones to rise continuously. The good news: exercise offers a scientifically proven way to effectively reduce stress and restore mental balance .
Why exercise is the natural stress reliever
Physical activity acts as a stress buffer on multiple levels. During exercise, our bodies release endorphins – natural happiness hormones that act as natural stress fighters. At the same time, stress hormones like cortisol and adrenaline, which are harmful when they occur chronically, are reduced.
Regular exercise also improves Quality of sleep, boosts the immune system and promotes concentration. These positive side effects create a stable basis for dealing with everyday challenges more calmly.
The 7 most effective sports for sustainable stress reduction
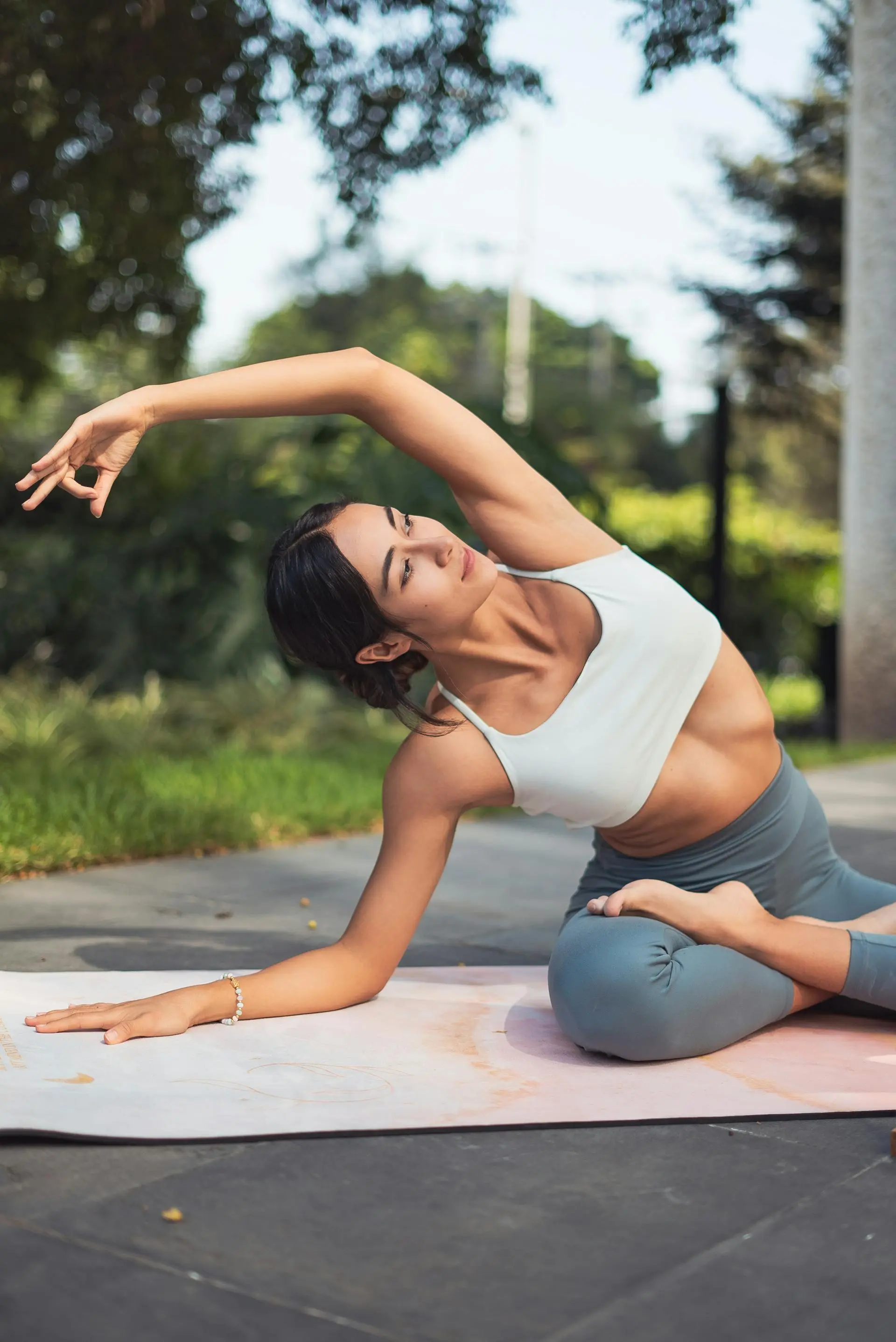
1. Yoga: Harmonizing body and mind
Yoga combines physical movement with conscious breathing and meditation. This holistic approach makes it particularly effective at reducing stress. Just 20 minutes Yoga a day can measurably lower cortisol levels.
Simple yoga exercise for beginners:
- Sit up straight and close your eyes
- Inhale slowly through the nose (4 seconds)
- Hold your breath (4 seconds)
- Exhale through the mouth (6 seconds)
- Repeat this breathing technique 10-15 times
2. Running: The classic for mental clarity
Endurance running is considered one of the most effective stress killers. The rhythmic movement and increased oxygen intake promote the release of endorphins. Many runners report the so-called "runner's high" – a feeling of deep relaxation and euphoria.













_1500x2250_150_RGB-2.webp)