© Rasi Bhadramani
Endocrinology
Treatment Methods
- Adrenal hyperplasia
- Gestational diabetes
- Growth disorders in children
- Hashimoto's thyroiditis
- Hormone deficiency
- Hormone-producing tumors
- Hyperthyroidism
- Hypofunction of the adrenal cortex
- Hypothyroidism
- MODY (Maturity Onset Diabetes of the Young)
- Obesity
- Osteoporosis
- Overactivity of the adrenal cortex
- Sex hormones
- Type 1 diabetes
- Type 2 diabetes
Endocrinology is a subdivision of internal medicine that deals with the diagnosis and treatment of diseases of the hormonal system. Hormones are biochemical messengers produced by special glands such as the thyroid, adrenal glands, pancreas, ovaries, or testes, and released into the blood. They control vital body functions such as metabolism, growth, reproduction, water balance, and various stress reactions. Accordingly, the spectrum of endocrinological diseases is broad.
These include, among others, diabetes mellitus, thyroid diseases, and autoimmune diseases such as Hashimoto's and Basedow's disease. Other important conditions include adrenal gland disorders, pituitary gland diseases such as Addison's disease, or hormone-producing tumors. Growth disorders in children, osteoporosis in old age and disorders of the sex hormones are also part of the field of endocrinology.
Hormone therapy and pharmaceutical regulation in endocrinology
Endocrine diseases can affect people of all ages – from childhood to old age – and often manifest through non-specific symptoms such as fatigue , weight fluctuations, mood instability, or skin changes. Careful diagnostics, usually consisting of blood tests, imaging procedures, and function tests, are therefore crucial. high ageThe treatment depends on the underlying disease and can range from hormone therapy through to drug regulation and surgical interventions. Given the complexity of hormonal control circuits, endocrinologists often work closely with other disciplines such as
Gynecology , pediatrics, oncology, or neurology.The goal of endocrinological care is to balance hormonal imbalances, relieve symptoms, and sustainably improve the quality of life of patients.
Focus areas of endocrinology
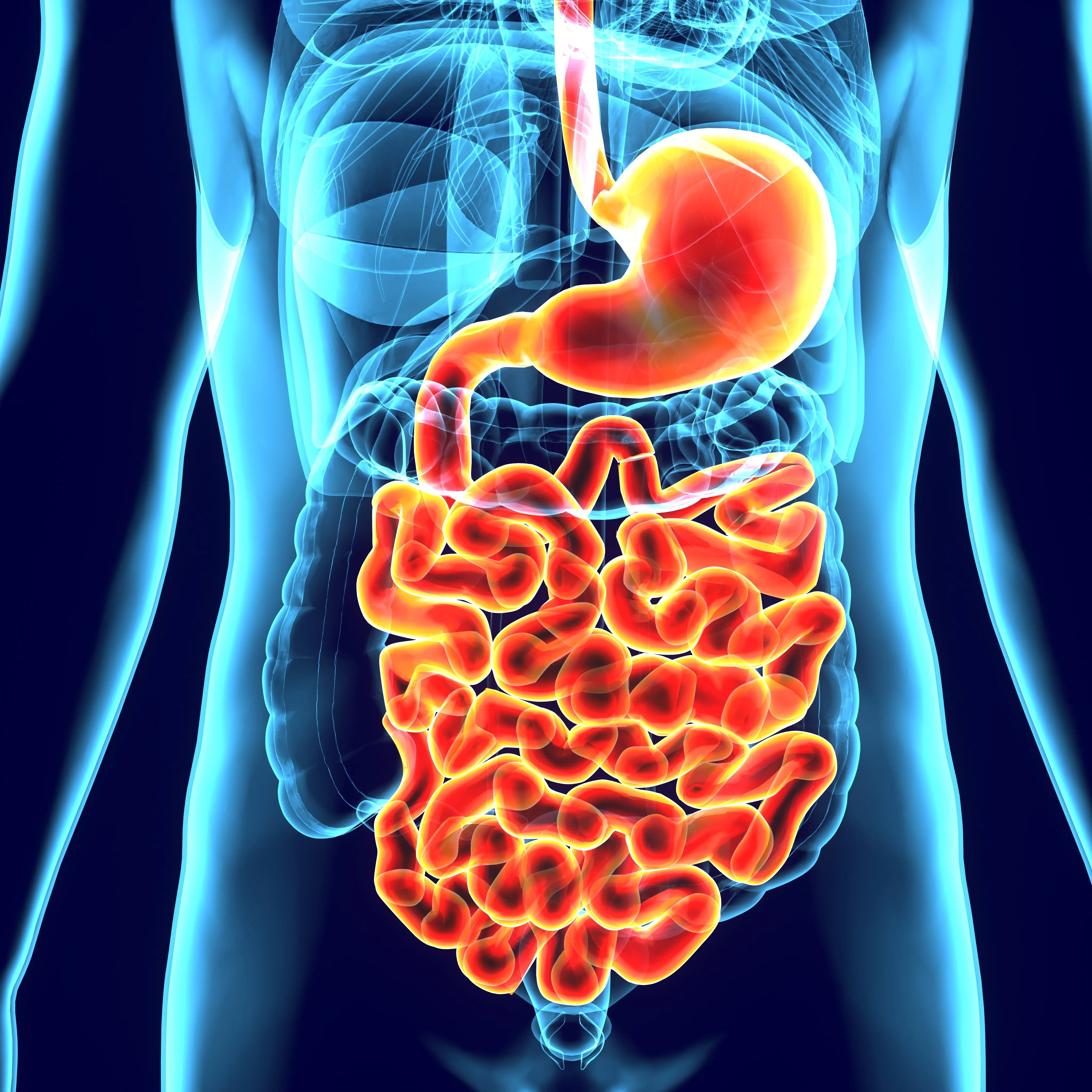
Diabetology
Diabetology represents a central focus within endocrinology. It deals with the research, diagnosis, treatment, and prevention of diabetes mellitus (commonly referred to as diabetes) and its complications. These primarily include the various types of diabetes mellitus: Type 1 diabetes and .Thyroid diseases
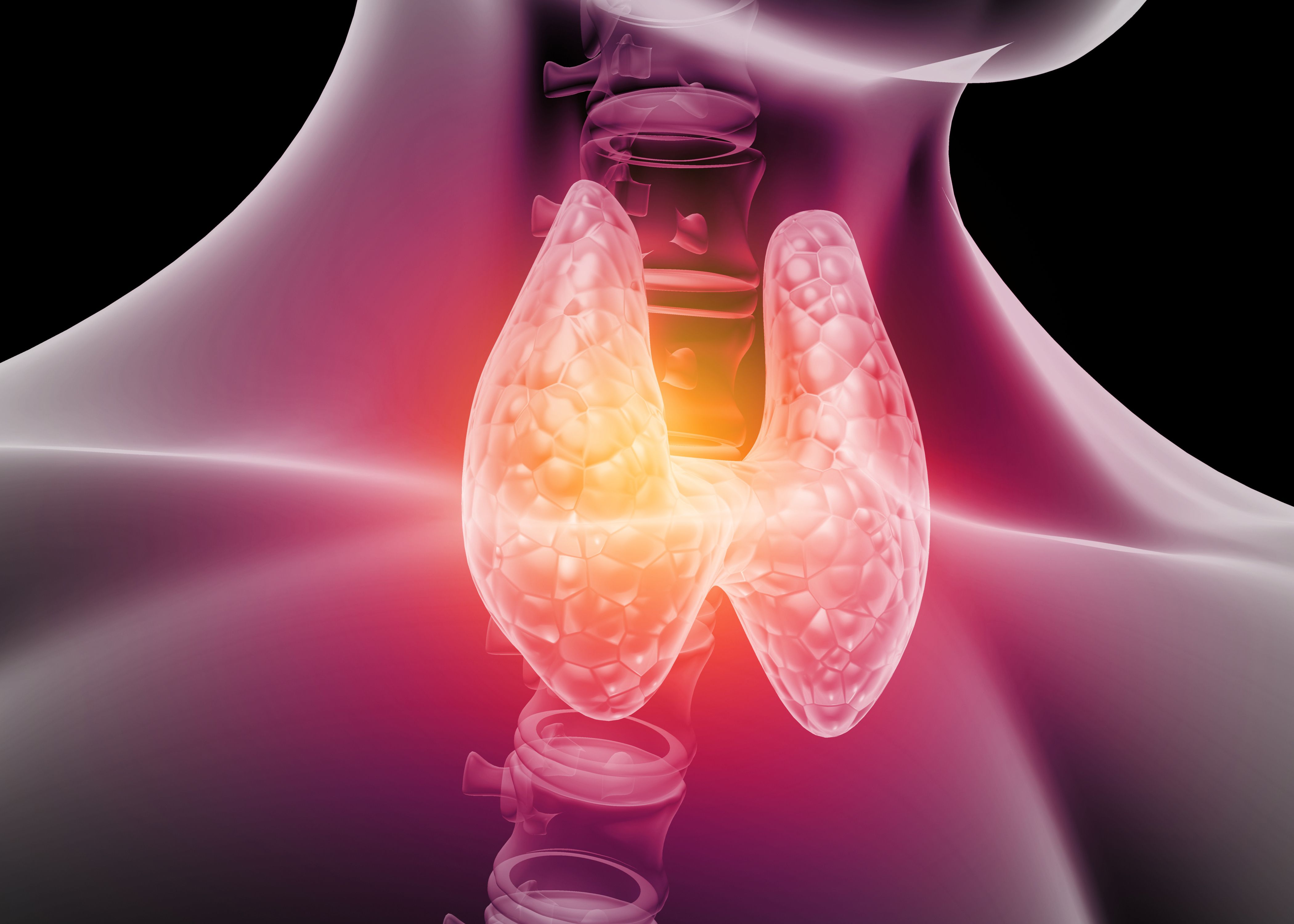
Thyroid diseases refer to a variety of functional and structural disorders of the thyroid, a hormone-producing gland in the neck area that plays an extremely central role in metabolism, circulation, and growth:
Hypothyroidism, Hyperthyroidism and Hashimoto's thyroiditis.
Adrenal gland disorders
Adrenal gland disorders are understood to be diseases that are either associated with overproduction or a deficiency of adrenal hormones. The adrenal gland consists of two parts - the adrenal cortex and the adrenal medulla - which produce different hormones. Disorders can affect both areas. Read more here: Adrenal cortex insufficiency, Overfunction of the adrenal cortex and Adrenal hyperplasia.
Diseases of the pituitary gland
The pituitary gland (hypophysis) is a small but very important hormone gland at the base of the brain. It controls many other glands in the body and influences growth, metabolism, reproduction, and stress reactions. Pituitary diseases are caused either by over- or underproduction of hormones or as a result of tumors, inflammations, or other structural damages. Learn more about the topic Hormone deficiency.








_1500x2250_150_RGB-2.webp)

