Other Treatment Methods

Breast augmentation
A breast augmentation is only advisable after puberty when the breast is fully developed.
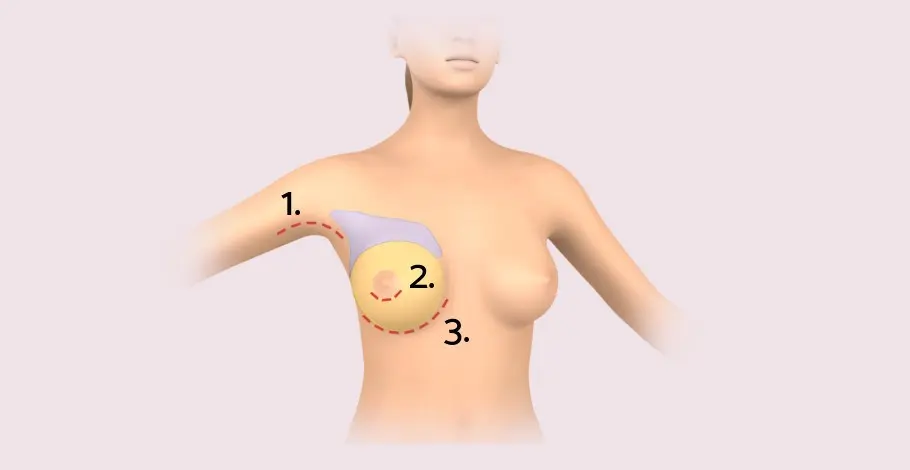
Procedure of breast augmentation
Breast augmentation can be done on an outpatient or inpatient basis. It takes one to one and a half hours and can be performed under general anesthesia or local anesthesia. The doctor makes an incision about four centimeters long either under the breast, in the armpit, or at the nipple. He then shapes a cavity behind the mammary gland or behind the chest muscle where he places the implant. After the skin is sutured, a firm bandage is applied.
Risks of breast augmentation
The body forms a capsule of connective tissue around the implant. This can harden or contract, necessitating further surgery. General surgical risks include bruising, bleeding, swelling, infections, and wound healing disorders or unsightly scars. In addition to a temporary feeling of numbness of the skin, permanent sensory disturbances on the skin of the breast are also possible. Sometimes the implants interfere with the assessment of the breast during a mammogram. Due to external violence or aging processes the implant may shift or become leaky. The implant may be visible or palpable through the skin.
After the operation
In the first few days, the breast bandage can be replaced with a specially fitted tight bra. This should be worn for two to three weeks. It is advisable to consistently use scar care for six months. to protect from the sun. They fade within months. Work and normal everyday activities are possible again after a few days. Sports are permitted no earlier than the sixth post-operative week, and only with a supportive sports bra. It takes months for the breast to fully adjust to the implant. Only then can the final result be evaluated.
Other Treatment Methods in this Department
Experts for this Treatment Method
All Experts in this Department
Show All- Aesthetic Surgery & Dermatology
Dr. Dr. Henrik Holtmann
LVATE Face Aesthetics an der Cecilienallee
- Aesthetic Surgery & Dermatology
Dr. med. Anna Brandenburg
Dermatologische Privatpraxis Dr. Anna Brandenburg
- Aesthetic Surgery & Dermatology
Prof. Dr. med. Johannes a. Veit
Nasenchirurgie München
- Aesthetic Surgery & Dermatology
Dr. med. Hanna M. D. Halter
Derma Marienplatz
- Aesthetic Surgery & Dermatology
Dr. med. Anette Zimpfer-Keese
Dres. Zimpfer/Zimpfer-Keese MVZ
- Aesthetic Surgery & Dermatology