Nearsightedness, medically known as myopia is one of the most common vision disorders worldwide. Those affected struggle to see distant objects clearly, whereas close objects appear sharply. Over the past decades, the number of nearsighted people has dramatically increased, especially in industrialized countries and urban areas.
What exactly is nearsightedness?
With nearsightedness, the eye is either too long or the corneal and lens refractive power is too strong. As a result, light rays are focused in front of the retina instead of directly on it. The outcome: distant objects appear blurry and indistinct, while close objects can be seen clearly.
The degree of nearsightedness is measured in diopters, with negative values indicating the refractive error. Mild myopia ranges from -0.25 to -3.0 diopters, moderate ranges from -3.0 to -6.0 diopters, and high myopia is above -6.0 diopters.
Causes of nearsightedness: Why does myopia occur?
Genetic factors
Hereditary factors play a crucial role in the development of myopia. If both parents are myopic, there is about a 60 percent chance that the child will also develop myopia. With one myopic parent, the risk is reduced to about 25 percent.
Environmental factors and lifestyle
Modern lifestyles significantly promote the development of myopia:
Close work and screen time.
Lack of daylight.
UrbanizationIn cities, the rate of myopia is significantly higher than in rural areas, which is associated with reduced viewing distances and less time spent outdoors.
Developmental factors
Most people develop myopia during school years when the eye is still growing. Increased near work while learning and reduced outdoor activities reinforce this trend.
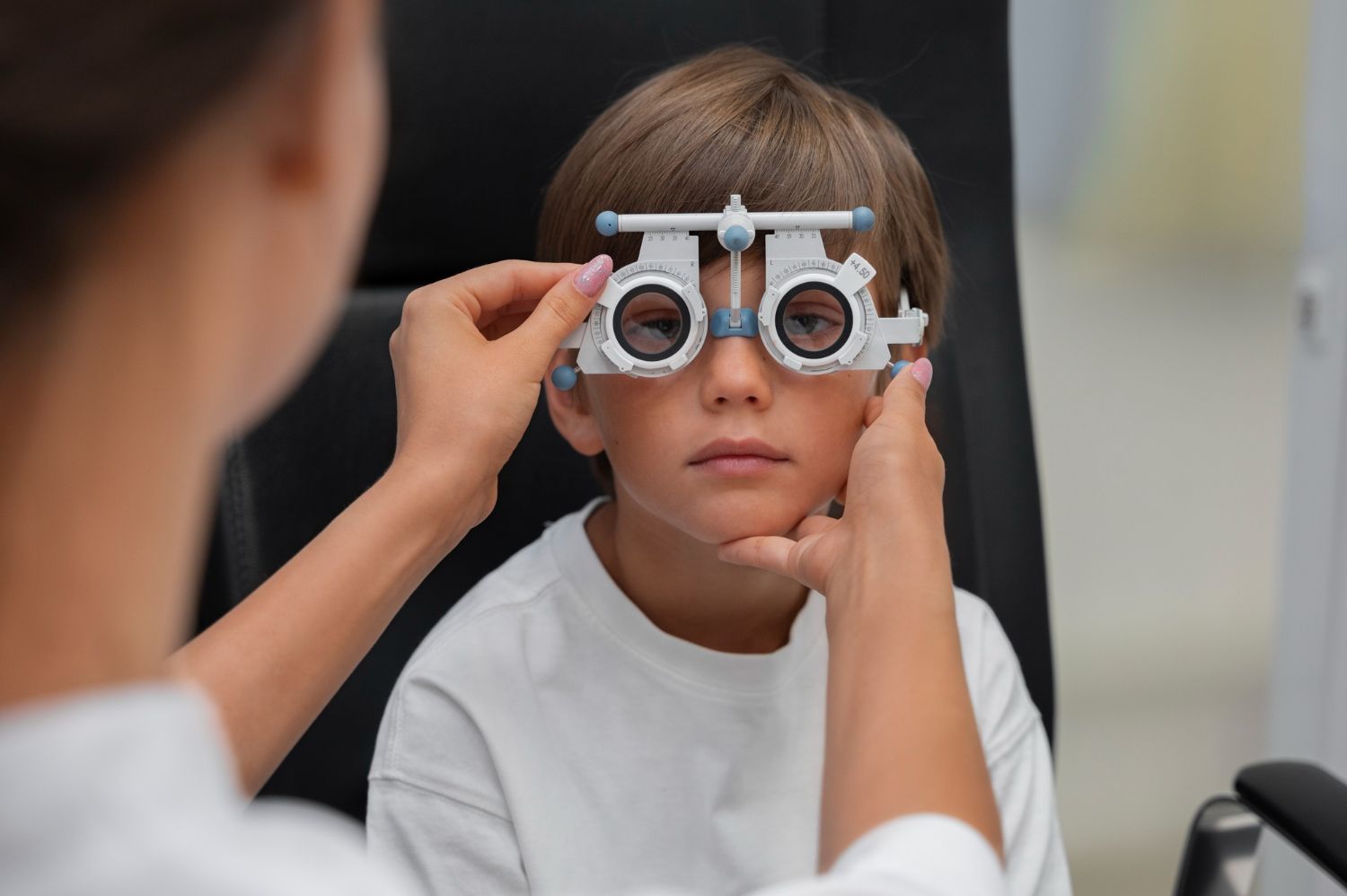
Recognizing symptoms: How do I notice myopia?
The signs of beginning or progressing myopia are usually clearly noticeable:
Main symptoms:
- Blurred distance vision (road signs, board contents, faces)
- Frequent squinting when looking at a distance
- Headaches after prolonged eye strain
- Tired, burning eyes especially in the evening